Grammar – Infinitive Phrases
Next Lesson
Summary
The content delves into the structure and function of infinitives and infinitive phrases in English grammar, highlighting their roles and forms within sentences.
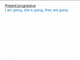
- Infinitives are formed by adding the preposition 'to' to the base form of a verb.
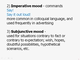
- Infinitive phrases extend infinitives by including additional predicate elements, acting as larger grammatical units.
- Both infinitives and infinitive phrases can serve as nouns within sentences, capable of being subjects or objects.
- An infinitive phrase can have its own subject, introduced by the preposition 'for'.
- The use of infinitives extends to being subjects of sentences, infinitives of purpose, and direct objects by idiom for specific verbs.
Chapters
00:04
Understanding Infinitives
00:20
Exploring Infinitive Phrases
00:41
Functional Roles of Infinitives and Phrases
01:16
Subjective Use of Infinitives